Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To assess the efficacy and tolerability of orlistat (Xenical®) in producing and maintaining weight loss over a 12-month period.
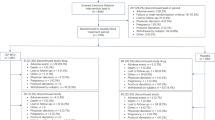
DESIGN: Patients were randomized to double-blind treatment with either orlistat 120 mg or placebo three times daily, in conjunction with a low-energy diet, for 12 months.
SETTING: Five centres in the UK.
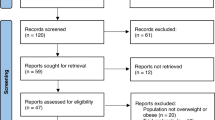
SUBJECTS: 228 obese adult patients with body mass index between 30 and 43 kg/m2 and mean weight 97 kg (range 74–144 kg).
INTERVENTIONS: All patients were prescribed a low-energy diet, providing 30% of energy from fat, designed to produce an individually tailored energy deficit of approximately 600 kcal/day, for a run-in period of 4 weeks and then 12 months, plus orlistat 120 mg or placebo three times daily.
MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Change in body weight (the primary efficacy parameter), waist circumference and adverse events were reviewed regularly, together with serum lipids, insulin, glucose and plasma levels of fat-soluble vitamins and β carotene.
RESULTS: Based on an intent-to-treat analysis, after 1 y of treatment patients receiving orlistat had lost an average of 8.5% of their initial body weight compared with 5.4% for placebo-treated patients; 35% of the orlistat group lost at least 5% of body weight compared with 21% of the placebo group (P<0.05), and 28% and 17%, respectively (P=0.04) lost at least 10% of body weight. Orlistat-treated patients showed significant decreases (P<0.05) in serum levels of total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, and in the low density lipoprotein:high density lipoprotein ratio in comparison with placebo. Both groups had similar adverse-event profiles, except for gastrointestinal events, which were 26% more frequent in the orlistat group but were mostly mild and transient. To maintain normal plasma levels of fat-soluble vitamins, supplements of vitamins A, D and E were given to 1.8%, 8.0% and 3.6%, respectively, of orlistat-treated patients, compared with 0.9% of placebo-treated patients for each vitamin type. After 1 y, the decrease in vitamin E and β carotene was significantly greater in orlistat-treated patients compared with those receiving placebo (P<0.001). No significant change was found in the mean vitamin E:total cholesterol ratio in either group after 52 weeks.
Conclusions: Orlistat, in conjunction with a low-energy diet, produced greater and more frequent significant weight loss than placebo during 1 y of treatment. One-third of orlistat-treated patients achieved clinically relevant weight loss (≥5% initial body weight). There was also an improvement in relevant serum lipid parameters. Fat-soluble vitamin supplements may be required during chronic therapy. Orlistat was well tolerated and offers a promising new approach to the long-term management of obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higgins M, Kannel W, Garrison R, Pinsky J, Strokes J III . Hazards of obesity. The Framingham experience Acta Med Scand 1988 723 (Suppl): 23–36.
Pi-Sunyer FX . Medical hazards of obesity Ann Intern Med 1993 119: 655–660.
Department of Health . The health survey for England. HMSO: London, 1998.
Department of Health . The health of the nation: a strategy for health in England. HMSO: London, 1992.
Bouchard C (ed) . The genetics of obesity. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1994.
Prentice AM, Jebb SA . Obesity in Britain: gluttony or sloth? Br Med J 1995 7002: 437–439.
Hyman FN, Sempos E, Saltsman J, Glinsmann WH . Evidence for success of caloric restriction in weight loss and control. Summary of data from industry Ann Intern Med 1993 119: 681–687.
Goldstein DJ, Parvin JH . Long-term weight loss: the effect of pharmacologic agents Am J Clin Nutr 1994 60: 647–657.
A report by the Royal College of Physicians . Clinical management of overweight and obese patients with particular reference to the use of drugs. Royal College of Physicians, 1998.
Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, Schaff HV . Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine-phentermine New Engl J Med 1997 337: 581–588.
Cannistra LB, Davis SM, Bauman AG . Valvular heart disease associated with dexfenfluramine New Engl J Med 1997 337: 636.
Fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine withdrawn. Report from the Medicines Control Agency Curr Probl Pharmacovig 1997 23: 13–14.
Hauptman JB, Jeunet FS, Hartmann D . Initial studies in humans with the novel gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor Ro18-0647 (tetrahydrolipstatin) Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 309S–313S.
Zhi J, Melia AT, Guerciolini R, Chung J, Kinberg J, Hauptman JB, Patel IH . Retrospective population-based analysis of the dose–response (fecal fat excretion) relationship of orlistat in normal and obese volunteers Clin Pharmacol Ther 1994 56: 82–85.
Drent ML, Larsson I, William-Olsson T, Quaade F, Czubayko F, von Bergmann K, Strobel W, Sjöström L, van der Veen EA . Orlistat (RO 18-0647), a lipase inhibitor, in the treatment of human obesity: a multiple dose study Int J Obes 1995 19: 221–226.
Tonstad S, Pometta D, Erkelens DW, Ose L, Moccetti T, Schouten JA, Golay A, Reitsma J, Del Bufalo A, Pasotti E et al.The effect of the gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor, orlistat, on serum lipids and lipoproteins in patients with primary hyperlipidaemia Eur J Clin Pharmac 1994 46: 405–410.
Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, Boldrin M, Golay A, Koppeschaar HPF, Krempf M, for the European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group . Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients Lancet 1998 352: 167–172.
Davidson MH, Hauptman J, GiGirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D, Heimburger DC, Lucas CP, Chung J, Heymsfield SB . Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat JAMA 1999 281: 235–242.
Hollander PA, Elbein SC, Hirsch IB, Kelley D, McGill J, Taylor T, Weiss SR, Crockett SE, Kaplan RA, Comstock J, Lucas CP, Lodewick PA, Canovatchel W, Chung J, Hauptman J . Role of orlistat in the treatment of obese patients with type 2 diabetes Diabetes Care 1998 21: 1288–1294.
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network . The management of obese patients in Scotland—integrating a new approach in primary health care with a national prevention and management strategy. SIGN, Royal College of Physicians: Edinburgh, 1996.
Schofield WN . Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work; human nutrition Clin Nutr 1985 39C (Suppl 1): 5–41.
Han TS, van Leer EM, Seidell JC, Lean MEJ . Waist circumference as a screening tool for cardiovascular risk factors: evaluation of Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) Obes Res 1996 4: 533–547.
Lean MEJ, Han TS, Morrison CE . Waist circumference as a measure for indicating need for weight management Br Med J 1995 311: 158–161.
Guy-Grand B, Apfelbaum M, Crepaldi G, Gries A, Lefebvre P, Turner P . International trial of long-term dexfenfluramine in obesity Lancet 1989 2: 1142–1145.
Lissner L, Heitmann BL . Dietary fat and obesity: evidence from epidemiology. Eur J Clin Nutr 1995 49: 79–90.
Goldstein DJ . Beneficial health effects of modest weight loss Int J Obes 1992 6: 397–415.
Williamson DF, Pamuk E, Thun M, Flanders D, Byers T, Heath C . Prospective study of intentional weight loss and mortality in never-smoking US white women aged 40–64 years Am J Epidemiol 1995 141: 1128–1141.
Williamson DF, Pamuk E, Thun M, Flanders D, Byers T, Heath C . Prospective study of intentional weight loss and mortality in overweight white men aged 40–64 years Am J Epidemiol 1999 149: 491–503.
Lean MEJ, Powrie JK, Anderson AS, Garthwaite PH . Obesity, weight loss and prognosis in type 2 diabetes Diabetic Med 1990 7: 228–232.
Paumgartner G, Sauerbruch . Gallstones: pathogenesis Lancet 1991 338: 1117–1121.
Melia AT, Koss-Twardy SG, Zhi J . The effect of orlistat, an inhibitor of dietary fat absorption, on the absorption of vitamins A and E in healthy volunteers J Clin Pharmac 1996 36: 647–653.
Zhi J, Melia AT, Koss-Twardy SG, Arora S, Patel IH . The effect of orlistat, an inhibitor of dietary fat absorption, on the pharmacokinetics of β-carotene in healthy volunteers J Clin Pharmac 1996 36: 152–159.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by F Hoffmann-La Roche. The authors acknowledge and thank the medical staff, research nurses and dietitians for their work: Dr MK Sridhar, Mrs S Stump, Mrs M Martin, Dr R Stancio and Ms C Hankey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finer, N., James, W., Kopelman, P. et al. One-year treatment of obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study of orlistat, a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor. Int J Obes 24, 306–313 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801128
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801128
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy for obesity: moving towards efficacy improvement
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2024)
-
Obesity Pharmacotherapy: a Review of Current Practices and Future Directions
Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology (2023)
-
Blockade of CXXC5-dishevelled interaction inhibits adipogenic differentiation, obesity, and insulin resistance in mice
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Descriptive analysis of reported adverse events associated with anti-obesity medications using FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) databases 2013–2020
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy (2022)
-
Development and validation by statistical treatment of stability indicating RP-HPLC method for quantification of Orlistat in Orlistat-loaded solid dispersion
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2021)