Abstract
Purpose
To report initial results from a European ICU surveillance programme focussing on antibiotic consumption, microbial resistance and infection control.
Methods
Thirty-five ICUs participated during 2005. Microbial resistance, antibiotic consumption and infection control stewardship measures were entered locally into a web-application. Results were validated locally, aggregated by project leaders and fed back to support local audit and benchmarking.
Results
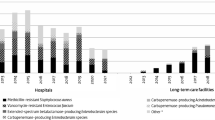
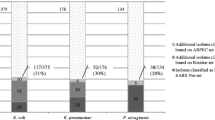
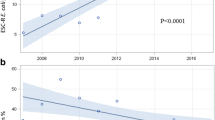
Median (range) antibiotic consumption was 1,254 (range 348–4,992) DDD per 1,000 occupied bed days. The proportion of MRSA was median 11.6% (range 0–100), for ESBL phenotype of E. coli and K. pneumoniae 3.9% (0–80) and 14.3% (0–77.8) respectively, and for carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa 22.5% (0–100). Screening on admission for alert pathogens was commonly omitted, and there was a lack of single rooms for isolation.
Conclusions
The surveillance programme demonstrated wide variation in antibiotic consumption, microbial resistance and infection control measures. The programme may, by providing rapid access to aggregated results, promote local and regional audit and benchmarking of antibiotic use and infection control practices.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vincent JL (2000) Microbial resistance: lessons from the EPIC study European Prevalence of Infection. Intensive Care Med 26(suppl 1):S3–S8
Hanberger H, Diekema D, Fluit A, Jones R, Struelens M, Spencer R, Wolff M (2001) Surveillance of antibiotic resistance in European ICUs. J Hosp Infect 48:161–176
Deplano A, Denis O, Poirel L, Hocquet D, Nonhoff C, Byl B, Nordmann P, Vincent JL, Struelens MJ (2005) Molecular characterization of an epidemic clone of panantibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 43:1198–1204
Vincent JL, Sakr Y, Sprung CL, Ranieri VM, Reinhart K, Gerlach H, Moreno R, Carlet J, Le Gall JR, Payen D (2006) Sepsis in European intensive care units: results of the SOAP study. Crit Care Med 34:344–353
Wroblewska MM, Rudnicka J, Marchel H, Luczak M (2006) Multidrug-resistant bacteria isolated from patients hospitalised in intensive care units. Int J Antimicrob Agents 4:285–289
Gastmeier P, Sohr D, Geffers C, Behnke M, Ruden H (2007) Risk factors for death due to nosocomial infection in intensive care unit patients: findings from the Krankenhaus Infektions Surveillance System. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 4:466–472
Hanberger H, Burman LG, Cars O, Erlandsson M, Gill H, Nilsson LE, Nordlinder D, Walther SM, ICU STRAMA Study Group (2007) Low antibiotic resistance rates in Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp but not in Enterobacter spp and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a prospective observational study in 14 Swedish ICUs over a 5-year period. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51:937–941
Tato M, Coque TM, Ruíz-Garbajosa P, Pintado V, Cobo J, Sader HS, Jones RN, Baquero F, Cantón R (2007) Complex clonal and plasmid epidemiology in the first outbreak of Enterobacteriaceae infection involving VIM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase in Spain: toward endemicity? Clin Infect Dis 45:1171–1178
Damas P, Ledoux D, Nys M, Monchi M, Wiesen P, Beauve B, Preiser JC (2008) Intensive care unit acquired infection and organ failure. Intensive Care Med 34:856–864
Brun-Buisson C (2008) ICU-acquired infections and sepsis: more of a deadly duo. Intensive Care Med 34:793–795
Monnet DL (2000) Toward multinational antimicrobial resistance surveillance systems in Europe. Int J Antimicrob Agents 15:91–101
Hanberger H, Arman D, Gill H, Kalenic S, Naaber P, Scicluna E, Suetens C (2008) CARE-ICU—Controlling Antibiotic REsistance in Intensive Care Units—First report from a web-based program for improved infection control in European ICUs. In: Programme of the 18th European congress of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases, Barcelona
Hanberger H, Erlandsson M, Burman LG, Cars O, Gill H, Lindgren S, Nilsson LE, Olsson-Liljequist B, Walther S, the ICU-STRAMA Study Group (2004) High antibiotic susceptibility among bacterial pathogens in Swedish ICUs. Report from a nation-wide surveillance program using TA90 as a novel index of susceptibility. Scand J Infect Dis 36:24–30
Hanberger H, Monnet DL, Nilsson LE (2005) Intensive care unit. In: Gould I, van der Meer J (eds) Antibiotic policies. Theory and practice. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 261–271
Erlandsson M, Burman LG, Cars O, Gill H, Nilsson LE, Walther SM, Hanberger H, the STRAMA ICU Study Group (2007) Prescription of antibiotic agents in Swedish intensive care units is empiric and precise. Scand J Infect Dis 39:63–69
de With K, Bergner J, Buhner R, de With K, Bergner J, Bühner R, Dörje F, Gonnermann C, Haber M, Hartmann M, Rothe U, Strehl E, Steib-Bauert M, Kern WV et al (2004) Antibiotic use in German university hospitals 1998–2000 (Project INTERUNI-II). Int J Antimicrob Agents 24:213–221
Muller A, Monnet DL, Talon D, Hénon T, Bertrand X (2006) Discrepancies between prescribed daily doses and WHO defined daily doses of antibacterials at a university hospital. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:585–591
Meyer E, Schwab F, Gastmeier P, Rueden H, Daschner FD, Jonas D (2006) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and antibiotic use in German intensive care units: data from Project SARI (Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in German Intensive Care Units). J Hosp Infect 64:238–243
Loeffler JM, Garbino J, Lew D, Harbarth S, Rohner P (2003) Antibiotic consumption, bacterial resistance and their correlation in a Swiss University Hospital and its adult intensive care units. Scand J Infect Dis 35:843–850
Lemmen SW, Häfner H, Kotterik S, Lütticken R, Töpper R (2000) Influence of an infectious disease service on antibiotic prescription behaviour and selection of multiresistant pathogens. Infection 28:384–387
Monnet DL SC, Jepsen OB (2000) Overall antimicrobial use and control strategies in intensive care units from 6 European countries. Abstract; 4th Decennial International Conference on Nosocomial and Healthcare-Associated Infections. CDC/SHEA, Atlanta
Goldmann DA, Weinstein RA, Wenzel RP, Tablan OC, Duma RJ, Gaynes RP, Schlosser J, Martone WJ (1996) Strategies to prevent and control the emergence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms in hospitals. A challenge to hospital leadership. JAMA 275:234–240
Björholt I, Haglind E (2004) Cost-savings achieved by eradication of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (EMRSA)-16 from a large teaching hospital. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:688–695
Lucet J-C, Paoletti X, Lolom I, Paugam-Burtz C, Trouillet J-L, Timsit J-F, Deblangy C, Andremont A, Regnier B (2005) Successful long-term program for controlling methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in intensive care units. Intensive Care Med 31:1051–1057
Raineri E, Crema L, De Silvestri A, Acquarolo A, Albertario F, Carnevale G, Latronico N, Petrosillo N, Tinelli C, Zoncada A, Pan A (2007) Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus control in an intensive care unit: a 10 year analysis. J Hosp Infect 67:308–315
Nulens E, Broex E, Ament A, Deurenberg RH, Smeets E, Scheres J, van Tiel FH, Gordts B, Stobberingh EE (2008) Cost of the meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus search and destroy policy in a Dutch University Hospital. J Hosp Infect 68:301–307
Harbarth S, Fankhauser C, Schrenzel J, Christenson J, Gervaz P, Bandiera-Clerc C, Renzi G, Vernaz N, Sax H, Pittet D (2008) Universal screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at hospital admission and nosocomial infection in surgical patients. JAMA 299:1149–1157
Cepeda JA, Whitehouse T, Cooper B, Hails J, Jones K, Kwaku F, Taylor L, Hayman S, Cookson B, Shaw S, Kibbler C, Singer M, Bellingan G, Wilson AP (2005) Isolation of patients in single rooms or cohorts to reduce spread of MRSA in intensive-care units: prospective two-centre study. Lancet 365:295–304
Humphreys H (2008) Can we do better in controlling and preventing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the intensive care unit (ICU)? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27:409–413 Feb 13 (Epub ahead of print)
Landman D, Bratu S, Alam M, Quale J (2005) Citywide emergence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains with reduced susceptibility to polymyxin B. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:954–957
Falagas ME, Bliziotis IA (2007) Pandrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: the dawn of the post-antibiotic era? Int J Antimicrob Agents 29:630–636
Jonas D, Meyer E, Schwab F, Grundmann H (2008) Genodiversity of resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in relation to antimicrobial usage density and resistance rates in intensive care units. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 29:350–357
Carmeli Y, Troillet N, Eliopoulos GM, Samore MH (1999) Emergence of antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of risks associated with different anti-pseudomonal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1379–1382
Peña C, Guzmán A, Suarez C, Dominguez MA, Tubau F, Pujol M, Gudiol F, Ariza J (2007) Effects of carbapenem exposure on the risk for digestive tract carriage of intensive care unit-endemic carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in critically ill patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:1967–1971
Erlandsson M, Gill H, Nilsson LE, Giske, Jonas, Nordlinder D, Walther SM, Hanberger H (2008) Antibiotic susceptibility patterns and clones of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients in Swedish ICUs. Scand J Infect Dis 40:487–494
Bonten MJ, Weinstein RA (2006) Antibiotic cycling in intensive care units: the value of organized chaos? Crit Care Med 34:549–551
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to all contributors in the CareICU network (see below), Fredrik Husander for web design and Mercedes Palomar and Dominique Monnet for valuable help with design of the questionnaire. The network was funded by the European Commission Directorate General for Health and Consumer Protection (DG SANCO) through the project Improving Patient Safety in Europe (IPSE, http://ipse.univ-lyon1.fr). Funding was also received from the Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control (www.smittskyddsinstitutet.se). Contributors: Ante Sekulic, Kresimir Oremus, Ljiljana Betica Radic, Marina Payerl Pal, Radovan Radonic, and Smilja Kalenic in Croatia; Václav Vaniš and Vlastimil Jindrak in the Czech Republic; Paul Naaber and Piret Mitt in Estonia; Anikó Farkas, Karolina Böröcz, Andrea Kurcz, Piroska Orosi, Erzsébet Rákay and Erika Rauth in Hungary; Elizabeth Scicluna in Malta; Monica Licker in Romania; Anita Johansson, Anne-Li Öhlin Gustafsson, Hans Blomqvist, Jonas Swanberg and Margareta Lannér Sjöberg in Sweden and Cengiz Uzun, Dilek Arman, Davut Ozdemir and Murat Dizbay in Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanberger, H., Arman, D., Gill, H. et al. Surveillance of microbial resistance in European Intensive Care Units: a first report from the Care-ICU programme for improved infection control. Intensive Care Med 35, 91–100 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1237-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1237-y