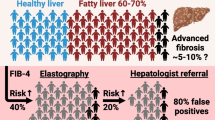
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a spectrum of liver pathologies characterized by hepatic steatosis with a history of little to no alcohol consumption or secondary causes of hepatic steatosis. The prevalence of NAFLD is 20–25 % of the general population in the Western countries and is associated with metabolic risk factors such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. The spectrum of disease ranges from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Advanced fibrosis is the most significant predictor of mortality in NAFLD. It is crucial to assess for the presence and degree of hepatic fibrosis in order to make therapeutic decisions and predict clinical outcomes. Liver biopsy, the current gold standard to assess the liver fibrosis, has a number of drawbacks such as invasiveness, sampling error, cost, and inter-/intra-observer variability. There are currently available a number of noninvasive tests as an alternative to liver biopsy for fibrosis staging. These noninvasive fibrosis tests are increasingly used to rule out advanced fibrosis and help guide disease management. While these noninvasive tests perform relatively well for ruling out advanced fibrosis, they also have limitations. Understanding the strengths and limitations of liver biopsy and the noninvasive tests is necessary for deciding when to use the appropriate tests in the evaluation of patients with NAFLD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanyal AJ. AGA technical review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1705–1725.
Craft S. Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer disease: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2006;20:298–301.
Monteiro R, Azevedo I. Chronic inflammation in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. doi:10.1155/2010/289645.
Afdhal NH. Management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 60-year-old man with probable nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: weight reduction, liver biopsy, or both? JAMA. 2012;308:608–616.
Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology. 2003;37:917–923.
Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–690.
Ogden C, Carroll M, Kit B, Flegal K. Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among US children and adolescents, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307:483–490.
Fatty NN, Disease L, Mulhall BP, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231.
Anstee QM, Targher G, Day CP. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:330–344.
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023.
Sheth SG, Gordon FD, Chopra S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:137–145.
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395.
Ekstedt M, Hagström H, Nasr P, Fredrikson M, Stål P, Kechagias S, et al. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. 2015;61:1547–1554.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2467–2474.
Nalbantoglu I, Brunt EM. Role of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:9026–9037.
Afdhal NH, Nunes D. Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1160–1174.
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, et al. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1898–1906.
Manning DS, Afdhal NH. Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1670–1681.
Kelleher TB, Afdhal N. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:667–683.
McPherson S, Stewart SF, Henderson E, Burt AD, Day CP. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2010;59:1265–1269.
Sheth SG, Flamm SL, Gordon FD, Chopra S. AST/ALT ratio predicts cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:44–48.
Ohgo H, Yokoyama H, Hirose H, et al. Significance of ALT/AST ratio for specifying subjects with metabolic syndrome in its silent stage. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. 2009;3:3–6.
Sorbi D, Boynton J, Lindor KD. The ratio of aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase: potential value in differentiating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from alcoholic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:1018–1022.
Ruffillo G, Fassio E, Alvarez E, et al. Comparison of NAFLD fibrosis score and BARD score in predicting fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;54:160–163.
Lee TH, Han SH, Yang JD, Kim D, Ahmed M. Prediction of advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an enhanced model of BARD score. Gut Liver. 2013;7:323–328.
Rodrigues S, Rodrigues-Pinto E, Albuquerque A, et al. Significant correlation between liver stiffness, liver histology, and APRI score. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. doi:10.1038/ajg.2012.271.
Pissaia A, Borderie D, Bernard D, Scatton O, Calmus Y, Conti F. APRI and FIB-4 scores are useful after liver transplantation independently of etiology. Transplant Proc. 2009;41:679–681.
Tapper EB, Krajewski K, Lai M, et al. Simple non-invasive biomarkers of advanced fibrosis in the evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterol Rep. 2014;2:276–280.
Angulo P, Bugianesi E, Bjornsson ES, et al. Simple noninvasive systems predict long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2013. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.06.057.
Harrison SA, Oliver D, Arnold HL, Gogia S, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Development and validation of a simple NAFLD clinical scoring system for identifying patients without advanced disease. Gut. 2008;57:1441–1447.
Cichoż-Lach H, Celiński K, Prozorow-Król B, Swatek J, Słomka M, Lach T. The BARD score and the NAFLD fibrosis score in the assessment of advanced liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18:CR735–CR740.
Ratziu V, Giral P, Charlotte F, et al. Liver fibrosis in overweight patients. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:1117–1123.
Syn WK, Choi SS, Diehl AM. Apoptosis and cytokines in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13:565–580.
Diab DL, Yerian L, Schauer P, et al. Cytokeratin 18 fragment levels as a noninvasive biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in bariatric surgery patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:1249–1254.
Feldstein AE, Wieckowska A, Lopez AR, Liu YC, Zein NN, McCullough AJ. Cytokeratin-18 fragment levels as noninvasive biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicenter validation study. Hepatology. 2009;50:1072–1078.
Cusi K, Chang Z, Harrison S, et al. Limited value of plasma cytokeratin-18 as a biomarker for NASH and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2014;60:167–174.
Pimentel CMG, Jiang Z, Otsubo T, Feldbrügge L, Challies T, Nasser I, et al. Poor inter-test reliability between CK18 kits as a biomarker of NASH. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61:905–912.
Friedrich-Rust M, Rosenberg W, Parkes J, Herrmann E, Zeuzem S, Sarrazin C. Comparison of ELF, FibroTest and FibroScan for the non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:103.
Guha IN, Parkes J, Roderick P, et al. Noninvasive markers of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: validating the European liver fibrosis panel and exploring simple markers. Hepatology. 2008;47:455–460.
Parkes J, Guha IN, Roderick P, et al. Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) test accurately identifies liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18:23–31.
Parkes J, Roderick P, Harris S, et al. Enhanced liver fibrosis test can predict clinical outcomes in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut. 2010;59:1245–1251.
Sumida Y, Yoneda M, Hyogo H, et al. Validation of the FIB4 index in a Japanese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:2.
Adler M, Gulbis B, Moreno C, et al. The predictive value of FIB-4 versus FibroTest, APRI, FibroIndex and Forns index to noninvasively estimate fibrosis in hepatitis C and nonhepatitis C liver diseases. Hepatology. 2008;47:762–763.
Lassailly G, Caiazzo R, Hollebecque A, et al. Validation of noninvasive biomarkers (FibroTest, SteatoTest, and NashTest) for prediction of liver injury in patients with morbid obesity. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23:499–506.
Ratziu V, Giral P, Munteanu M, et al. Screening for liver disease using non-invasive biomarkers (FibroTest, SteatoTest and NashTest) in patients with hyperlipidaemia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:207–218.
Oh S, Afdhal NH. Hepatic fibrosis: are any of the serum markers useful? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2001;3:12–18.
Ratziu V, Massard J, Charlotte F, et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (FibroTest-FibroSURE) for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:6.
Leroy V, Sturm N, Faure P, et al. Prospective evaluation of FibroTest®, FibroMeter®, and HepaScore® for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: comparison with hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2014;61:28–34.
Calès P, Boursier J, Oberti F, et al. FibroMeters: a family of blood tests for liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008;32:40–51.
Becker L, Salameh W, Sferruzza A, et al. Validation of Hepascore, compared to simple indices of fibrosis, in US patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:696–701.
Bonder A, Tapper EB, Afdhal NH. Contemporary assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2015;19:123–134.
Suzuki A, Angulo P, Lymp J, Li D, Satomura S, Lindor K. Hyaluronic acid, an accurate serum marker for severe hepatic fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2005;25:779–786.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45:846–854.
Tanwar S, Trembling PM, Guha IN, et al. Validation of terminal peptide of procollagen III for the detection and assessment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2013;57:103–111.
Lee SS, Park SH, Kim HJ, et al. Non-invasive assessment of hepatic steatosis: prospective comparison of the accuracy of imaging examinations. J Hepatol. 2010;52:579–585.
van Werven JR, Marsman HA, Nederveen AJ, et al. Assessment of hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing liver resection: comparison of US, CT, T1-weighted dual-echo MR imaging, and point-resolved 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 2010;256:159–168.
Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, et al. The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:745–750.
Saverymuttu SH, Joseph AE, Maxwell JD. Ultrasound scanning in the detection of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;292:13–15.
Hepburn MJ, Vos JA, Fillman EP, Lawitz EJ. The accuracy of the report of hepatic steatosis on ultrasonography in patients infected with hepatitis C in a clinical setting: a retrospective observational study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2005;5:14.
Rofsky NM, Fleishaker H. CT and MRI of diffuse liver disease. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1995;16:16–33.
Borra RJH, Salo S, Dean K, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: rapid evaluation of liver fat content with in-phase and out-of-phase MR imaging. Radiology. 2009;250:130–136.
Kim D, Kim WR, Talwalkar JA, Kim HJ, Ehman RL. Advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography. Radiology. 2013;268:411–419.
Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Wang Z, et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:440–451.e6.
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:32–40.
http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf12/K123806.pdf (cited 2015 Aug 30).
Wong VWS, Vergniol J, Wong GLH, et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:454–462.
Nobili V, Vizzutti F, Arena U, et al. Accuracy and reproducibility of transient elastography for the diagnosis of fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2008;48:442–448.
Bonder A, Afdhal N. Utilization of FibroScan in clinical practice. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2014;16:1–7.
Tapper EB, Castera L, Afdhal NH. FibroScan (vibration-controlled transient elastography): where does it stand in the United States practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.039.
Cassinotto C, Lapuyade B, Mouries A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis with impulse elastography: comparison of supersonic shear imaging with ARFI and FibroScan®. J Hepatol. 2014;61:550–557.
Coco B, Oliveri F, Maina AM, et al. Transient elastography: a new surrogate marker of liver fibrosis influenced by major changes of transaminases. J Viral Hepat. 2007;14:360–369.
Kim KM, Choi WB, Park SH, et al. Diagnosis of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by transient elastography in asymptomatic healthy individuals: a prospective study of living related potential liver donors. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:382–388.
Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, et al. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:343–350.
Mueller S, Millonig G, Sarovska L, et al. Increased liver stiffness in alcoholic liver disease: differentiating fibrosis from steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:966–972.
Pais R, Lupşor M, Poantă L, et al. Liver biopsy versus noninvasive methods—fibroscan and fibrotest in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of the literature. Rom J Intern Med. 2009;47:331–340.
Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R, et al. Feasibility and diagnostic performance of the FibroScan XL probe for liver stiffness measurement in overweight and obese patients. Hepatology. 2012;55:199–208.
Nahon P, Kettaneh A, Tengher-Barna I, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2008;49:1062–1068.
Fraquelli M, Rigamonti C, Casazza G, et al. Etiology-related determinants of liver stiffness values in chronic viral hepatitis B or C. J Hepatol. 2011;54:621–628.
Arena U, Vizzutti F, Corti G, et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology. 2008;47:380–384.
Wong VWS, Vergniol J, Wong GLH, et al. Liver stiffness measurement using XL probe in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:1862–1871.
Millonig G, Reimann FM, Friedrich S, et al. Extrahepatic cholestasis increases liver stiffness (fibroScan) irrespective of fibrosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:1718–1723.
Millonig G, Friedrich S, Adolf S, et al. Liver stiffness is directly influenced by central venous pressure. J Hepatol. 2010;52:206–210.
Goertz RS, Egger C, Neurath MF, Strobel D. Impact of food intake, ultrasound transducer, breathing maneuvers and body position on acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastometry of the liver. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33:380–385.
Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, Cholongitas E, Davidson BR, Burroughs AK. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol. 2015;54:650–659.
Crespo G, Fernández-Varo G, Mariño Z, et al. ARFI, FibroScan®, ELF, and their combinations in the assessment of liver fibrosis: a prospective study. J Hepatol. 2012;57:281–287.
Rotman Y, Koh C, Zmuda JM, Kleiner DE, Liang TJ. The association of genetic variability in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) with histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;52:894–903.
Valenti L, Al-Serri A, Daly AK, et al. Homozygosity for the patatin-like phospholipase-3/adiponutrin I148M polymorphism influences liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:1209–1217.
Dongiovanni P, Romeo S, Valenti L. Genetic factors in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:460190.
Liu Y-L, Patman GL, Leathart JBS, et al. Carriage of the PNPLA3 rs738409 C>G polymorphism confers an increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2015;61:75–81.
Liu Y-L, Reeves HL, Burt AD, et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. 2014. doi:10.1038/ncomms5309.
Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Scian R, et al. Genetic variation in transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and histological disease severity. Hepatology. 2015;61:515–525.
Calès P, Lainé F, Boursier J, et al. Comparison of blood tests for liver fibrosis specific or not to NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2009;50:165–173.
Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, Tetri BN, Contos MJ, Sanyal AJ. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1104–1112.
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, et al. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and FibroTest. Hepatology. 2007;46:32–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dharmesh Kaswala MD: None. Michelle Lai MD: None. Nezam H Afdhal MD: Consultant: EchoSens, Sandhill Scientific, Chief Medical Officer, Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaswala, D.H., Lai, M. & Afdhal, N.H. Fibrosis Assessment in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in 2016. Dig Dis Sci 61, 1356–1364 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4079-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4079-4